Multienterprise Collaboration Network
Moving from Silos to connected enterprises for operational efficiency and cost savings
What are Multienterprise Collaboration Networks (MCN)?
Gartner defines multienterprise collaboration networks (MCNs) as solutions that support a community of trading partners of any tier and type that need to coordinate and execute on business processes extending across multiple enterprises. Gartner considers cloud-based MCNs to be a key technology to coordinate, orchestrate and automate an organization’s extended supply chain within the overall business ecosystem they operate in. The key capabilities of MCN solutions include three layers: Network representation and management, Application functions, Embedded analytics and intelligence.
Connecting, coordinating, collaborating and executing on business processes that extend across multiple enterprises for joint value generation will allow supply chain organizations to drive resilience in times of disruptions and address the following top priorities:
- Transparency: Having end-to-end visibility and allowing close to real-time collaboration to avoid and respond to disruptions
- Productivity: Increasing productivity and efficiency to drive financial outcome
- Resilience: Taking the right actions to meet customer needs while protecting the brand
- Sustainability: Supporting environmental, social and governance (ESG) initiatives, including emissions and carbon footprint
Why Multienterprise Collaboration Network Solution?
In its latest Market Guide for MCN, Gartner highlights the relevance of Multienterprise Collaboration Networks in addressing today’s business challenges such as supply chain disruptions and environmental risks. To tackle these challenges, creating resilient and sustainable supply chains as well as collaborating in a multitier environment across multiple levels is the way to go.
Despite increasing disruption, many companies still lack the ability to gain a more holistic, end-to-end view of what is happening in and with their supply chains. For this reason, MCNs have never been more important.
Disclaimer:
Gartner, Market Guide for Multienterprise Collaboration Networks, Christian Titze, Brock Johns, 18 April 2023
GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission.
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
Organizations leverage MCNs for multiple reasons
- Improving end-to-end supply chain visibility
- Tightening relationships and collaboration with business partners
- Simplifying data connectivity and data capture activities
- Reducing integration effort and cost having to maintain fewer point-to-point interfaces
- Utilizing integrated workflows between supply chain functions
- Modernizing legacy application portfolios along a cloud-first strategy
- Fostering joint value generation
- Improving operational outcome
The Current MCN Solutions in marketplace
In order to achieve multienterprise collaboration, solution providers have developed solutions that can connect multiple enterprises for data and document interchange, and facilitate collaboration limited to specific functions. These solutions are mainly grouped as below:
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) It is a standardized electronic communication method that enables the exchange of business documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, between trading partners in a structured, computer-readable format. EDI eliminates the need for paper-based transactions and allows for a more efficient and accurate exchange of information between businesses. It is commonly used in supply chain management and various industries to streamline communication and transactions between different organizations. The EDI are limited in their scope of deployment as the business ecosystem is not limited to a few enterprises.
- Customer – Vendor Portals also termed as Procure to Pay (P2P) and Order to Cash (O2C) are those solutions which allow data transactions to be entered by vendors or customers for a manufacturer or distributor and is integrated to the main solution of the manufacturer or distributor. These solutions are not multienterprise collaboration softwares in true sense as they are limited to one principal and do not create a network or pear-2-peer collaboration. Some ERP software provider have built-in functions whereas majority of them rely on third party solutions. These solutions help the manufacturer or distributor to cut down data digitization but increases the workload of the vendors and customers. The vendor and customers maintain separate software for managing their business as they are not the exclusive supplier or customer.
- Vendor Managed Inventory & Collaborative Replenishment - VMI enables manufacturers, and their supply chain partners, to share real-time inventory data to create a lean, demand-driven supply chain including better product forecasts, optimized shipments, and improved in-stock rates.
- Layer-based multienterprise collaboration solutions are being offered by some solution providers where every enterprise intending to be part of a network has to onboard on the specified solution. Though it resolves the supply chain issues to some extent, but the enterprises have to maintain separate solution for managing their business.
Limitations of Collaboration Solutions on offer
The MCN solutions available in marketplace have inherent limitations, especially for SMBs.
- Maintaining Multiple IT Software solutions – The current solutions available in marketplace force enterprises to maintain at least two software solutions – one for multienterprise collaboration and the other for managing business functions.
- Escalated IT Cost – MCN solutions, being an additional service software solution, the IT cost gets escalated. Every enterprise is required to maintain an ERP software of their own to manage their business and operations. The additional software solution costs to the enterprises and may be prohibitive for low margin enterprises or SMBs.
- Increased Operational Cost – Enterprises have to hire additional resources to manage data in different portals which may be a negligible cost to larger organizations but may be cost burden to SMBs and low operating margin businesses.
- Data Digitization – Data is required to be digitized at least in two softwares demanding more resources to be deployed by enterprises which may outscore the benefits these solutions may offer to enterprises, especially to SMBs.
- Data Discrepancies– MCNs require data to be duplicated and maintained in two sets– one for the enterprise operations and the other one for the network. Maintaining data in two sets often results in errors of omission and commission and thus frequent rectification.
Scale of the Problem with EDI
While Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) can enhance collaboration among enterprises using such solutions, it doesn’t automatically resolve the challenge of data duplicity. EDI, itself, can be a complex deployment for a large business network. It may function well for a network of manageable enterprises, but for a more extensive network, it can become highly intricate and challenging to manage, not to mention the potential for prohibitive costs. The magnitude of the problem can be assessed from the illustration given below.
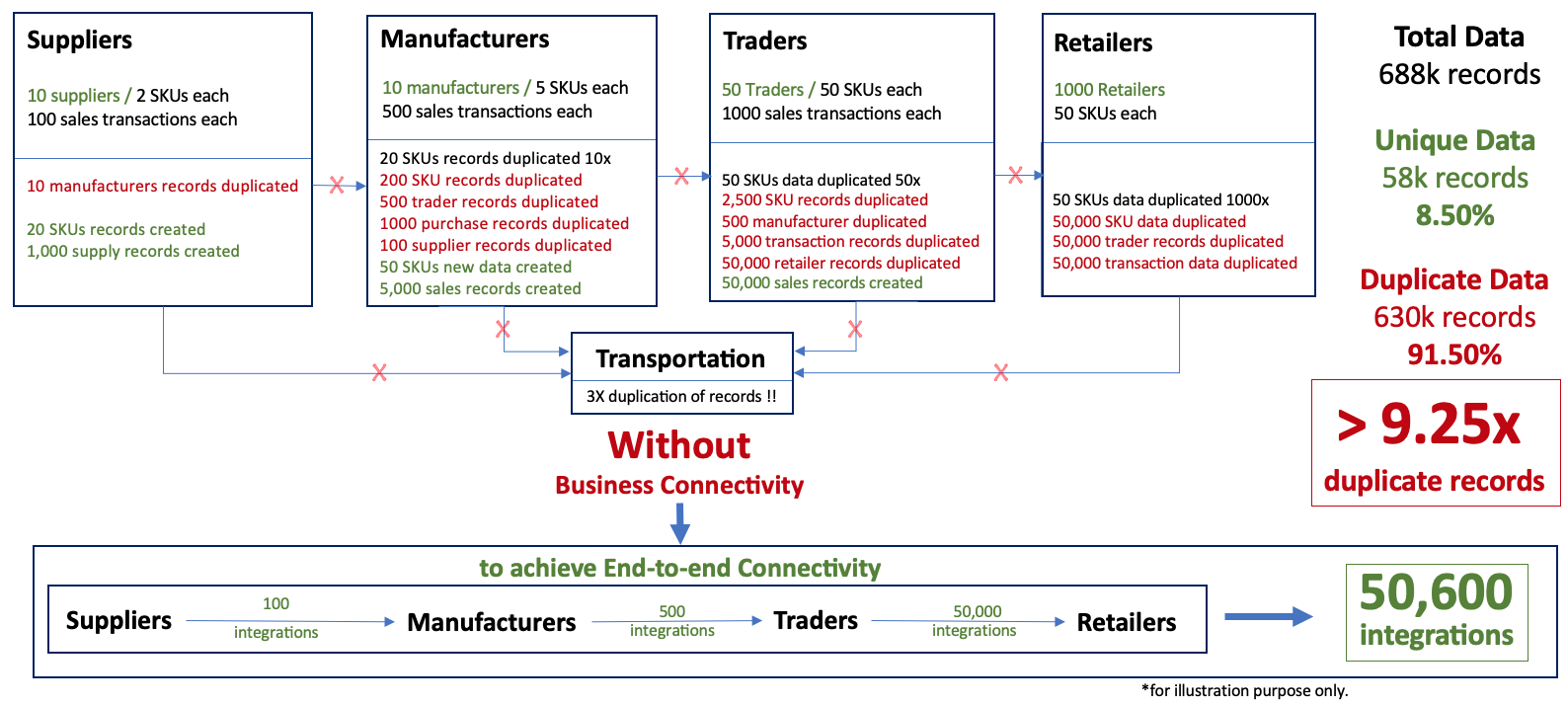
Barriers in Existing ERP Software to build a true MCN
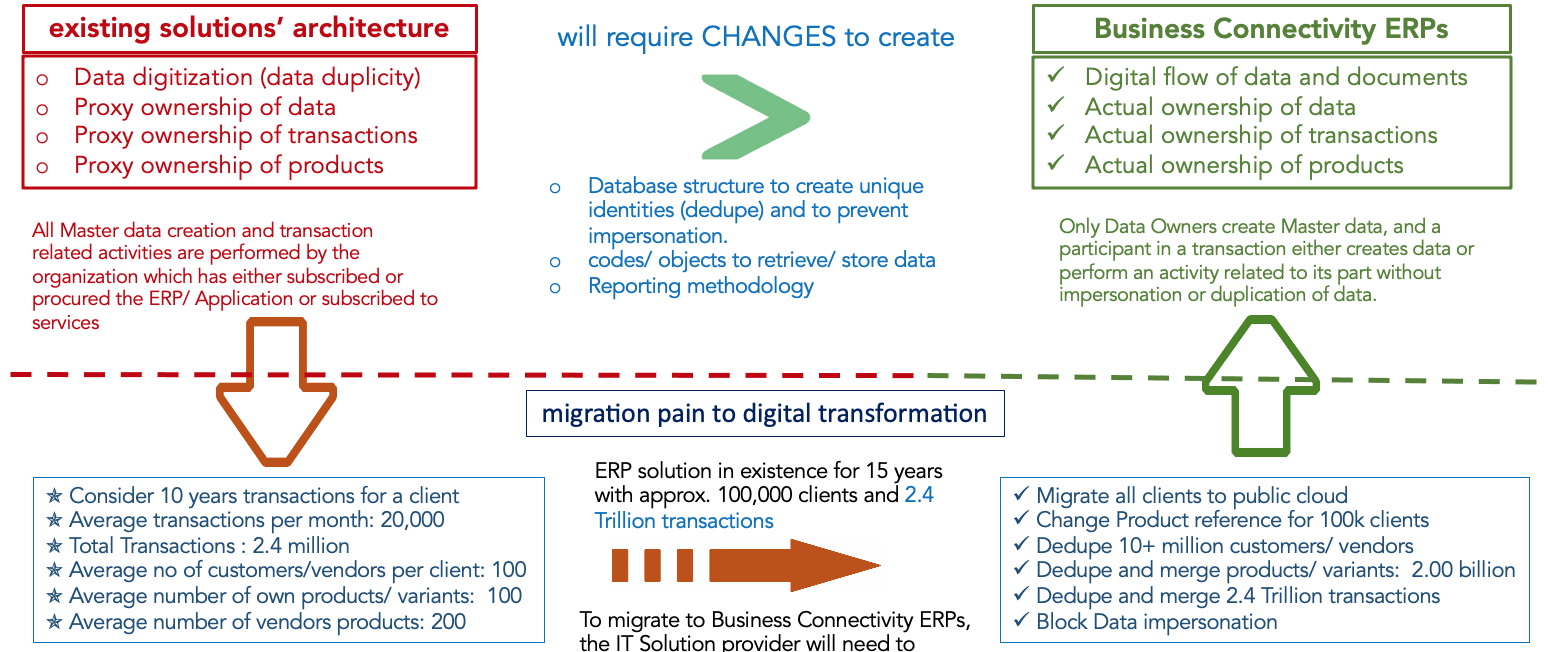
The existing ERP Software providers may find it difficult to transform their ERP softwares into a true MCN. When the architecture of the ERP software was designed, it considered an enterprise only and there was lack of focus or comprehension that it will need to communicate with other ERP softwares of other enterprises. As a result, each ERP software deployed by an enterprise or even the same ERP software deployed by different enterprises creates enterprise specific data sets resulting into duplicity of data and records to manage business of each of the enterprises.
If these long-standing ERP softwares decide to convert their ERP software into true MCN without requiring additional software or resources, it will require complete change of existing data structure and architecture and thus may not be possible as the cost may be exorbitant and migrating existing customers to a new architecture may result into data loss and redundancies. This can be illustrated as below:
Zumbido Express offers Virtual ERP
It’s a first of its kind offering in the world. When you onboard, you get a virtual ERP hosted on most secured cloud servers to manage all your business functions. The access to full featured ERP does away with need of managing multiple softwares and data duplication in each of them to manage business functions, right from managing your customers, human resources, financial transactions to order processing and inventory.


MCN Solutions have No Data Duplication
Why should you manage data for other organizations? Zumbido Express empowers subscribing organizations to own their data and manage themselves. Other subscribing organizations simply use your data to complete transactions with you. Thus, all your partners need not duplicate and manage your data separately to keep record of transactions that they carry out with you. No worries of incorrect or inconsistent data.
